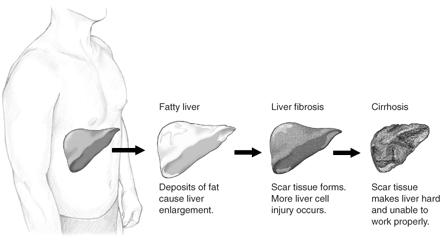
What is NAFLD?
NAFLD, also known as "Fatty Liver", is a condition where fat builds up in the liver, not caused by excessive alcohol consumption. It has two main forms:
- NAFL (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver): The mildest form, with fat accumulation but no inflammation or liver damage.
- NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis): A more serious form with inflammation and potential liver damage.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Insulin resistance: A key factor, leading to increased fat storage in the liver.
- Obesity: A major risk factor, with up to 90% of patients with severe obesity having NAFLD.
- Other factors: Genetics, metabolic disorders, certain medications, and unhealthy lifestyle choices.
Symptoms:
NAFLD often has no symptoms, but some people may experience:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Right upper abdominal discomfort
Diagnosis:
- Blood tests: To assess liver function and rule out other conditions.
- Imaging studies: Ultrasound is preferred, with CT or MRI as alternatives.
- Liver biopsy: May be necessary in certain cases to confirm NASH.
Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes: Weight loss, healthy diet, and regular exercise are crucial.
- Medications: Limited options, with some showing potential benefits for specific cases.
- Surgery: Bariatric surgery may be considered for patients with significant obesity.
Complications:
- In rare cases, NASH can progress to cirrhosis (scarring) and liver failure.
- Increased risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
Prognosis:
- NAFL generally has a good prognosis with proper management.
- NASH requires close monitoring and management to prevent complications.
Prevention:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a balanced diet
- Regular physical activity
- Limiting alcohol consumption
The Interprofessional Team:
- Physicians: Diagnose and manage NAFLD, prescribe medications, and perform procedures.
- Dietitians: Provide guidance on healthy eating habits.
- Exercise specialists: Develop personalized exercise programs.
- Mental health professionals: Support patients with lifestyle changes and manage stress1.
Diagnostics
| Date | Type | Value | Unit |
|---|